1. Introduction to Networks
- Network: A computer network is a collection of two or more interconnected devices (computers, printers, mobiles, servers, etc.) that can communicate and share resources (data, files, hardware, internet).
- Need for Networks:
- Resource sharing (printers, files, applications).
- Communication (email, chat, video conferencing).
- Data sharing and remote access.
2. Types of Networks
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- Covers a very small area (a few meters).
- Used for connecting personal devices like smartphones, laptops, printers, Bluetooth devices.
- Example: Bluetooth or USB tethering.
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- Covers a small geographical area (like an office, school, or building).
- High speed, inexpensive, privately owned.
- Example: Computer lab network in school.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Covers a city or a large campus.
- Larger than LAN but smaller than WAN.
- Example: Cable TV network, city-wide Wi-Fi.
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- Covers a very large geographical area (country, continent, or globe).
- Internet is the largest WAN.
- Example: Banking network across countries.
3. Network Devices
- Modem
- Converts digital signals (computer) into analog signals (telephone lines) and vice versa.
- Needed for internet connection over telephone lines.
- Hub
- A simple device that connects multiple computers in a network.
- Broadcasts data to all connected devices (less efficient).
- Switch
- Smarter than a hub; forwards data only to the intended device (using MAC address).
- Improves network efficiency.
- Repeater
- Amplifies and regenerates signals to extend the distance of a network.
- Router
- Connects multiple networks (LAN to the internet).
- Uses IP addresses to send data to correct destination.
- Gateway
- Acts as a translator between two different networks using different protocols.
- Example: Connecting LAN with mainframe system.
4. Network Topologies
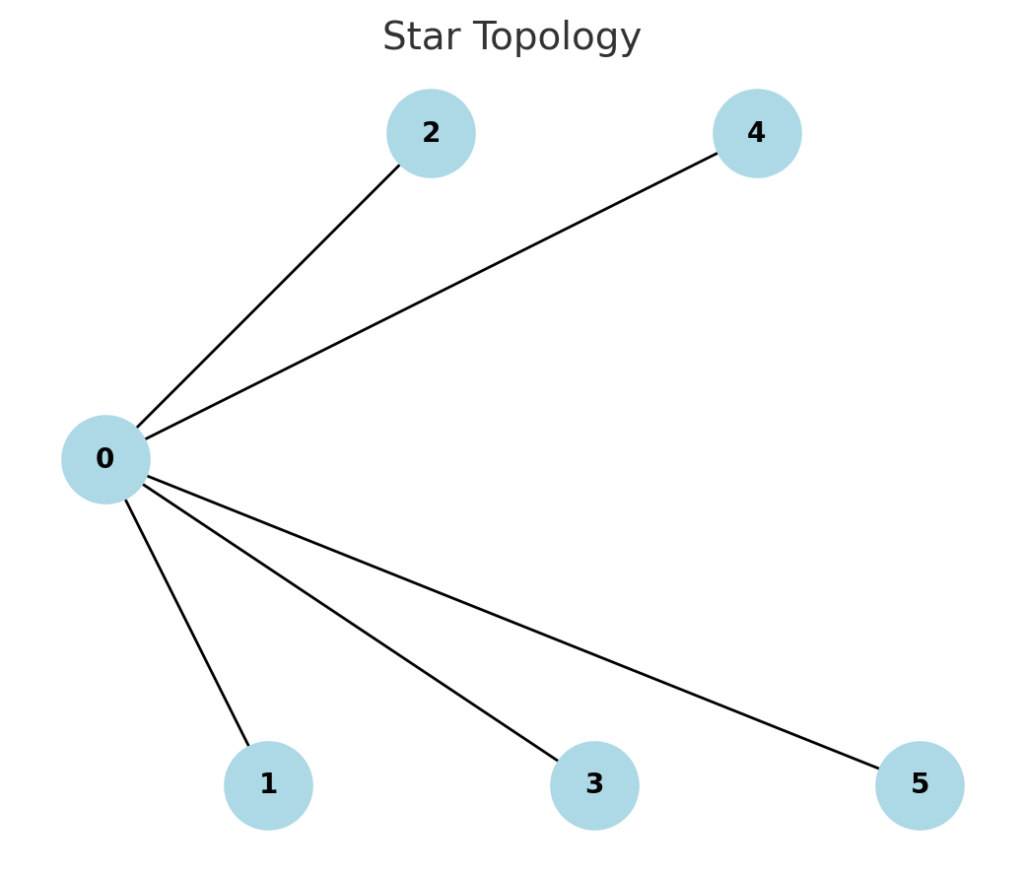
- Star Topology
- All devices connected to a central hub/switch.
- Easy to add/remove devices, but if hub fails, whole network fails.
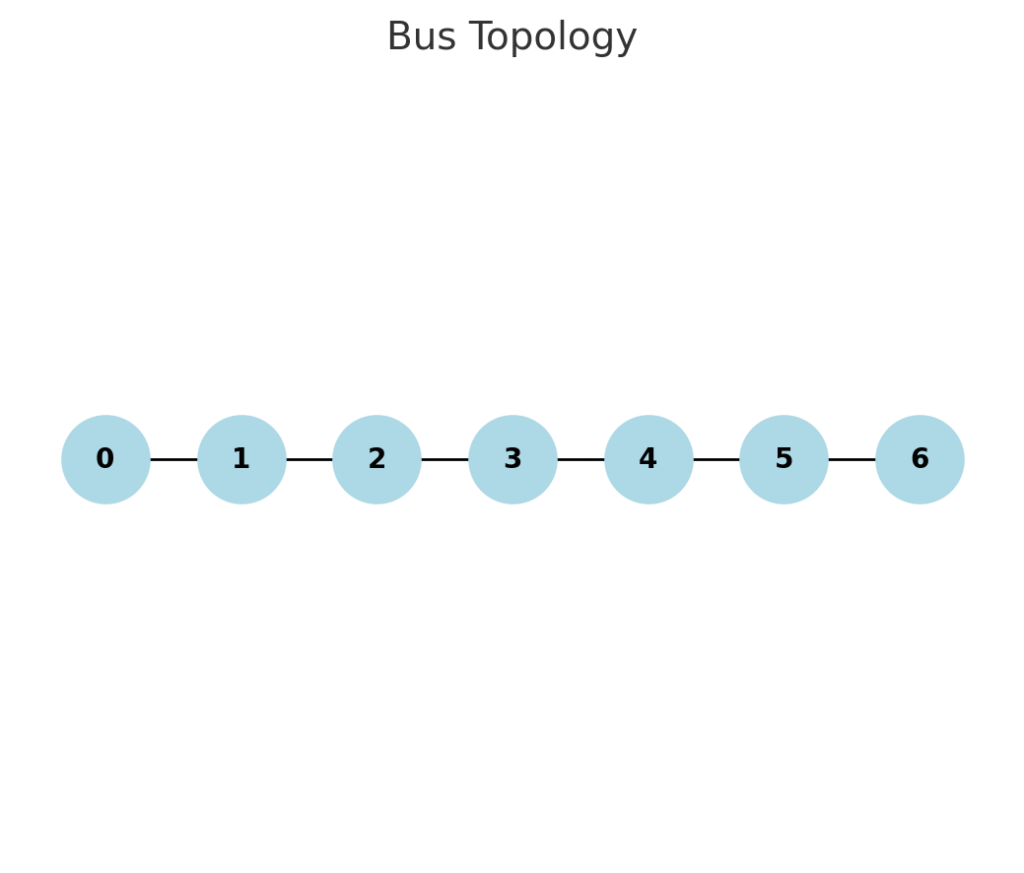
- Bus Topology
- All devices connected using a single backbone cable.
- Simple and cheap, but backbone failure crashes the entire network.
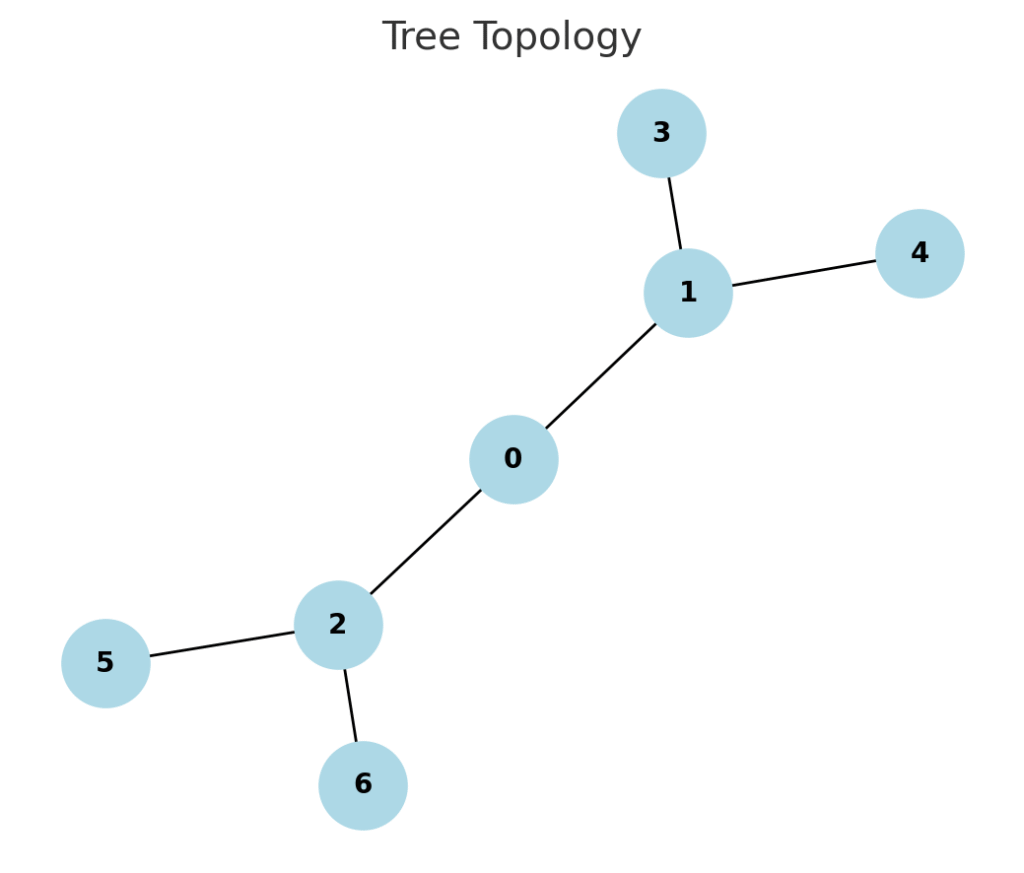
- Tree Topology
- Hierarchical structure combining star and bus topology.
- Good for large organizations.
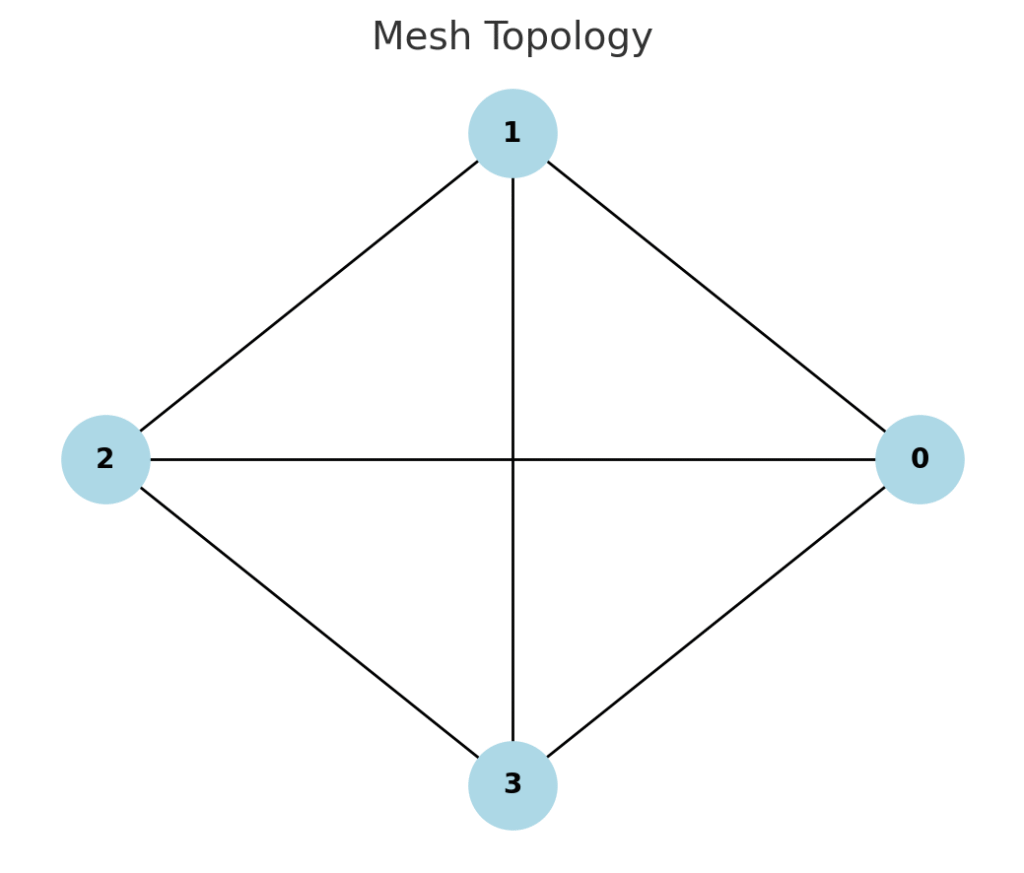
- Mesh Topology
- Every device connected to every other device.
- Very reliable (no single point of failure) but expensive.
5. Introduction to Internet
- Internet: A global network of interconnected networks, allowing data communication and resource sharing.
- Key Terms:
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator): Address of a resource on the internet (e.g.,
https://www.cbse.gov.in). - WWW (World Wide Web): A collection of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the internet.
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator): Address of a resource on the internet (e.g.,
Applications of Internet:
- Web: Browsing information on websites.
- Email: Sending/receiving electronic messages.
- Chat: Real-time text communication.
- VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol): Making voice/video calls over the internet (e.g., WhatsApp, Skype).
6. Website
- Website: A collection of related web pages hosted on a web server, accessible via a domain name (e.g., www.itxperts.co.in).
- Webpage: A single document/page on a website.
Difference between Website and Webpage
| Website | Webpage |
|---|---|
| Collection of related pages | A single page of a website |
| Example: www.wikipedia.org | Example: Wikipedia’s “India” page |
Static vs Dynamic Webpages
- Static Page: Fixed content, same for all users. Example: About Us page.
- Dynamic Page: Content changes based on user interaction or database. Example: Facebook feed, Amazon product page.
Web Server and Hosting
- Web Server: A computer that stores websites and delivers them to users on request (e.g., Apache, Nginx).
- Web Hosting: Renting space on a server to store a website and make it accessible on the internet.
7. Web Browsers
- Web Browser: Software used to access and view web pages.
- Common Browsers: Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Safari, Opera.
Browser Features:
- Settings – Customize homepage, privacy, security, download preferences.
- Add-ons & Plug-ins – Extra tools to enhance functionality (e.g., Ad-blocker, Flash Player, Grammarly).
- Cookies – Small text files stored by websites on user’s computer to remember preferences and track activity.
✅ Summary Points
- Network → PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN.
- Devices → Modem, Hub, Switch, Repeater, Router, Gateway.
- Topologies → Star, Bus, Tree, Mesh.
- Internet → URL, WWW, Applications (Web, Email, Chat, VoIP).
- Website vs Webpage → Static vs Dynamic.
- Web Server & Hosting.
- Browsers → Settings, Add-ons, Plug-ins, Cookies.
Practice Questions
A. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Which of the following is the largest network?
a) LAN
b) MAN
c) WAN
d) PAN - Which device connects different networks and directs data using IP addresses?
a) Hub
b) Switch
c) Router
d) Repeater - Which topology is most reliable but also most expensive?
a) Bus
b) Star
c) Tree
d) Mesh - The address
https://www.cbse.gov.inis an example of:
a) IP Address
b) URL
c) Domain Name System
d) Protocol - Cookies are used to:
a) Improve internet speed
b) Store user preferences and activity
c) Connect networks
d) Provide virus protection
Answer Key: 1–c, 2–c, 3–d, 4–b, 5–b
B. Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
- Define PAN with an example.
- Name any two commonly used web browsers.
- What does VoIP stand for?
- Write one difference between static and dynamic web pages.
- Which device is used to boost network signals?
C. Short Answer Questions (2–3 Marks)
- Differentiate between Hub and Switch.
- Write two advantages and disadvantages of Bus topology.
- What is a Web Server? Give two examples.
- Write two differences between a website and a webpage.
- Explain any two applications of the internet.
D. Long Answer Questions (4–5 Marks)
- Explain PAN, LAN, MAN, and WAN with examples.
- Discuss different network devices with their functions.
- Draw neat diagrams and explain Star, Bus, and Mesh topologies.
- What is a website? Explain static and dynamic webpages with suitable examples.
- What are web browsers? Explain features like settings, add-ons, plug-ins, and cookies.