
COMPUTER SCIENCE CLASS 12 PYTHON PROJECTS
Find the best CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Python projects with source code, practical file ideas, and guidance to excel...
Engineering Library
I am a full-stack web developer from India with over 8 years of experience in building dynamic and responsive web solutions. Specializing in both front-end and back-end development, I have a passion for creating seamless digital experiences. When I'm not coding, I enjoy sharing insights and tutorials on the latest web technologies, helping fellow developers stay ahead in the ever-evolving tech landscape.

Find the best CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Python projects with source code, practical file ideas, and guidance to excel...

Technology in 2025 isn’t just evolving—it’s rewriting the very rules of how we learn, code, and interact with machines. For...

1. Hello AI – Print “Hello AI World” 2. Fibonacci Sequence Generator (Recursion vs Iteration) 3. Tic-Tac-Toe with Minimax AI...
Meta is taking a bold step in the world of artificial intelligence by partnering with Midjourney, the popular generative art...

The world of Artificial Intelligence and Technology is booming like never before. Every day, we see new innovations that change...

The Indian gaming ecosystem is experiencing seismic shifts as major startups begin shuttering operations following the passage of comprehensive gaming...

OpenAI is making significant moves in the Indian market with the announcement of its first office in the country. The...

If you run a business, ranking on Google is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. Whether you own a local store,...
The AI landscape is experiencing a seismic shift. While chatbots dominated headlines throughout 2023 and early 2024, a new paradigm...
In the ever-evolving world of software development, few technologies have revolutionized how we build, ship, and run applications quite like...
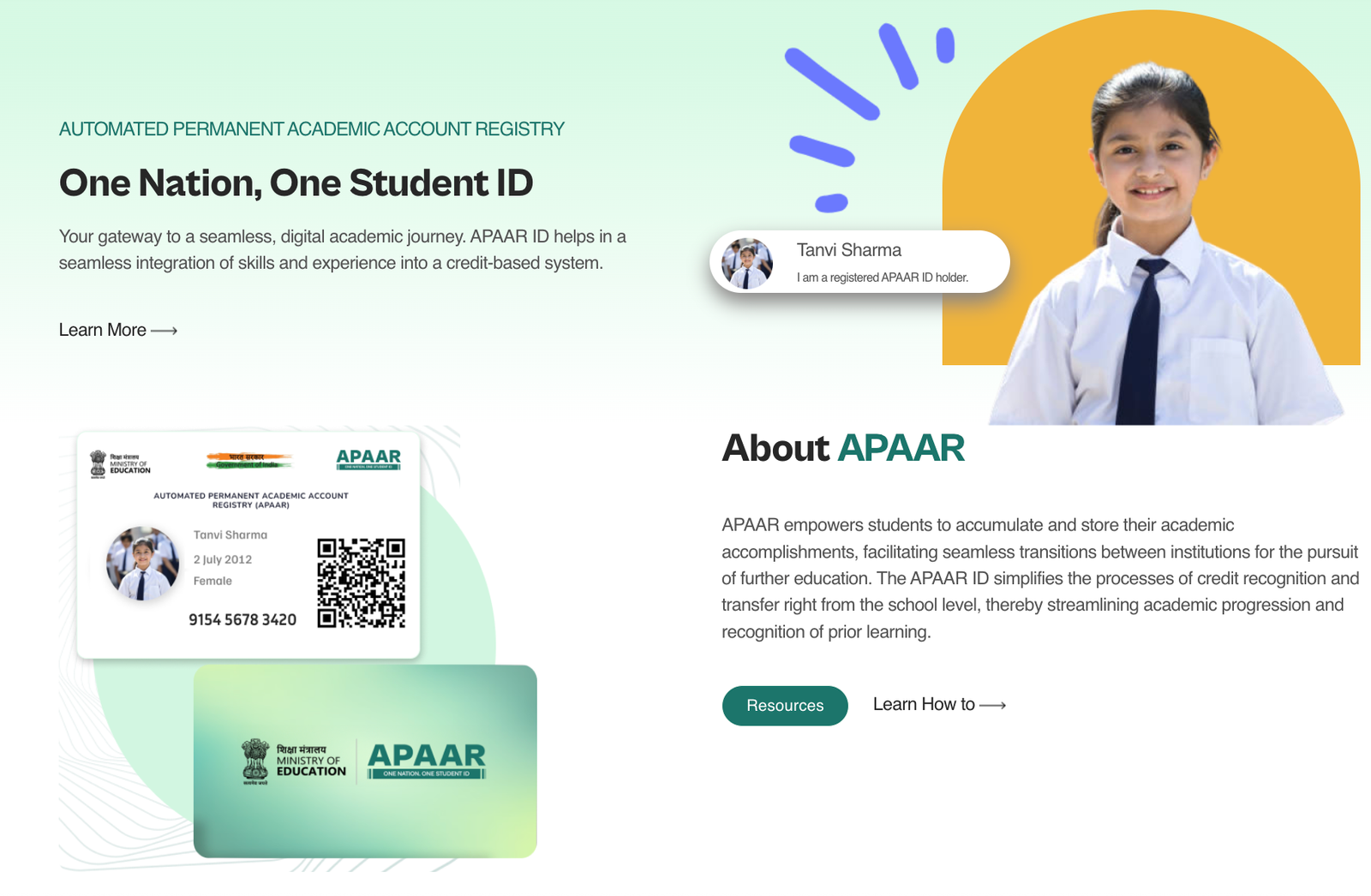
Why is an APAAR ID important?Every student needs an APAAR ID because it helps you get important services and resources...
India’s tech landscape is buzzing with AI innovation, but not every story is about success. Recently, Dhrub Rathi’s ambitious AI...
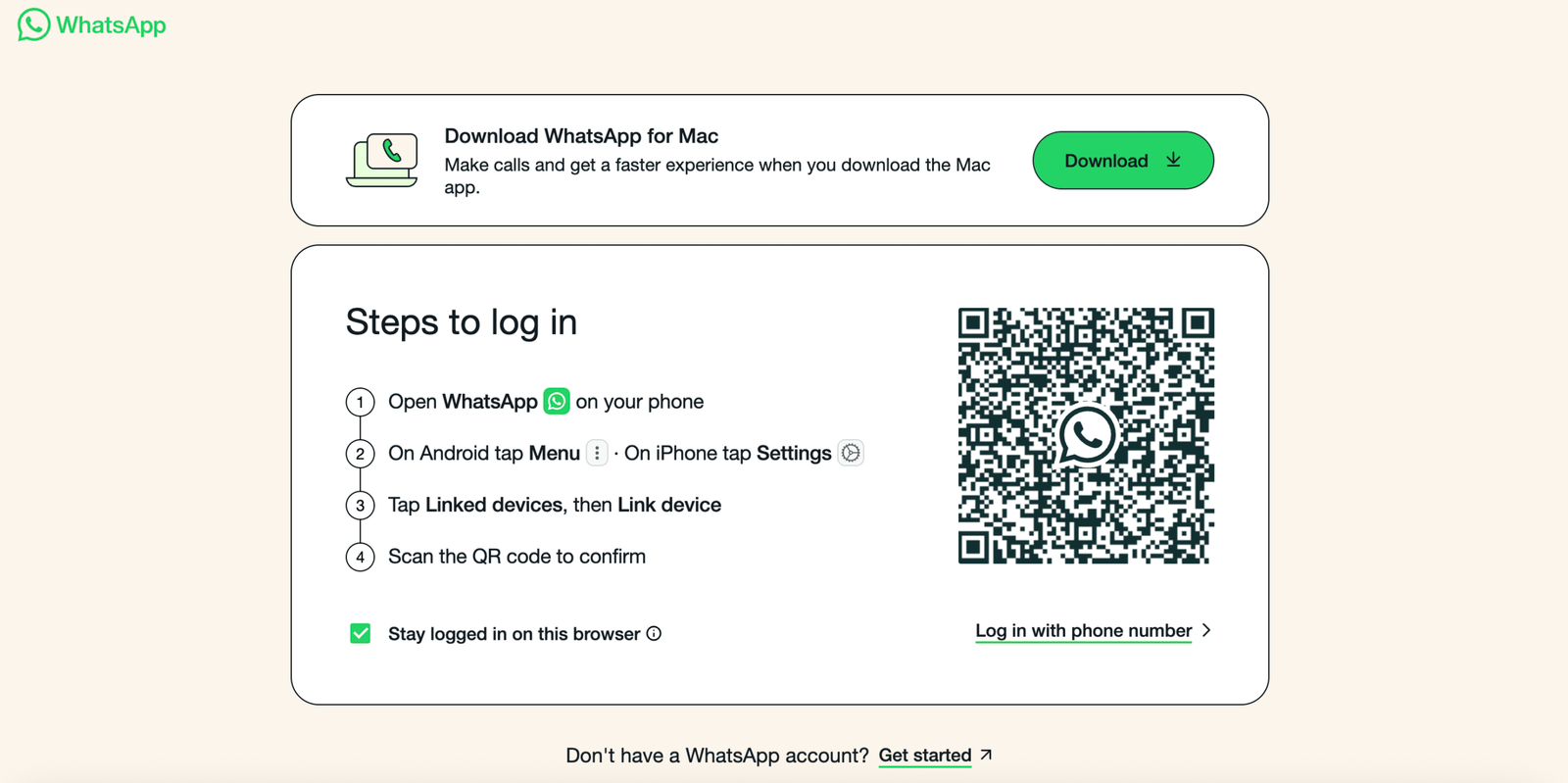
WhatsApp Web is a lifesaver when you want to manage chats directly from your computer. But sometimes, even with a...

A Costly Reversal In a shocking turn of events, the Pentagon has canceled two nearly completed human resources software projects—one...
OpenAI has just made artificial intelligence more accessible than ever before with the launch of ChatGPT Go, a revolutionary new...

In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence, accessing premium AI tools often means juggling multiple subscriptions, remembering different passwords,...
Over the past week, Linktree — the popular “link-in-bio” service used by millions of creators, small businesses, and organizations —...
Today’s rooftop solar inverters aren’t just power boxes—they’re networked computers connected to your Wi-Fi and, indirectly, to the grid. Vulnerabilities...

India’s IT services sector is in the middle of a quiet reset. After years of rapid hiring during the digital...

In a world full of advanced AI assistants, choosing the right tool can make a huge difference in productivity, creativity,...

FastAPI is a modern, high-performance web framework for building APIs with Python 3.8+ based on standard type hints. It’s built...

Introduction Artificial Intelligence is an exciting field and CBSE Class 10 AI curriculum encourages students to build simple, meaningful projects...
When working on Machine Learning models, one common challenge you’ll encounter is handling categorical data. Most ML algorithms work only...
Missing data is one of the most common challenges in any machine learning or data analysis project. If not handled...