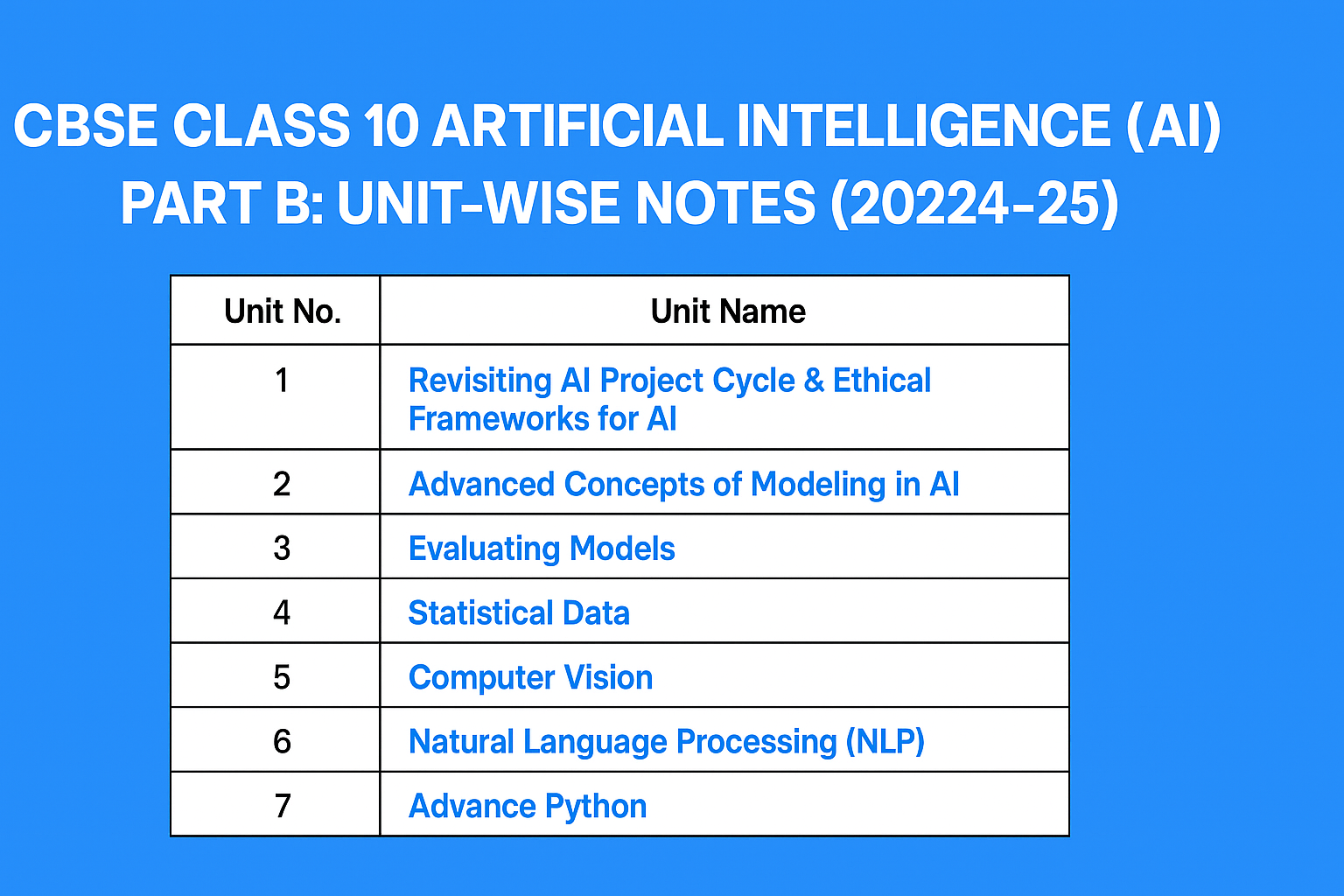
CBSE Class 10 Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Part B: Unit-Wise Notes (2024-25)
Explore detailed, easy-to-understand unit-wise notes for CBSE Class 10 Artificial Intelligence – Part B: Subject-Specific Skills as per the latest 2024-25 syllabus. Topics include AI project cycle, modeling, evaluation, statistical data, computer vision, NLP, and Python. Perfect for teachers and students for classroom learning and revision.